The NEG: Detailing the next steps
Last week energy ministers took an important step towards unifying climate and energy policy in Australia. The National Energy Guarantee (NEG) is the sixth attempt at national climate and energy policy in 11 years. The COAG Energy Council has supported further work on its detailed design for final sign off in August. So what have they actually agreed to and, most importantly, will it work?
The NEG is basically a policy framework which is bolted on to the existing design of the National Electricity Market (NEM). There are two explicit and one implicit setting for the NEG machine: it is designed to ensure a prescribed level of emissions and a prescribed level of reliability (notionally the existing reliability standard).
The NEG also implicitly requires attention on how we will manage energy security in the future. While reliability requires there is sufficient capacity to meet demand at any time in each region of the NEM, energy security requires power quality is maintained in each region, including frequency services and inertia. Provision of these services were relatively ubiquitous and costless when most generators were conventional. They become more important and valuable with increased generation from asynchronous generators.
Debate over the ambition of the NEG design with regard to emissions reductions misses the point. The NEG as proposed is a policy machine, designed to deliver whatever targets are set by government. It is important that the design is able to deliver efficient outcomes to meet all the required obligations as emissions targets increase over time, which they are likely to do.
The design as proposed provides a holistic mechanism by which:
- industry emissions can be reduced over time in a least-cost way;
- through the Reliability Guarantee, confidence in the NEM’s existing investment mechanism can be restored; and,
- much needed emissions policy clarity can be provided, lifting a tremendous risk burden which has beset the industry.
The Energy Security Board’s High Level Design Document has taken a big step forward in explaining the model and addresses much of the latent confusion in the industry. We unpack it to see what still needs to be done.
Emissions Guarantee – How it works
Within a central registry, after a compliance year retailers will have to identify a total amount of historical generated energy equivalent to their historical retail sales, and it must have an average emissions intensity below the government’s set target, measured in tonnes CO2 (equivalent) per MWh. They can choose whatever way they wish to obtain access to that generation, as long as it is only listed in the registry once. The paper includes some useful tables that show example techniques of how a retailer might source this generation, inter alia:
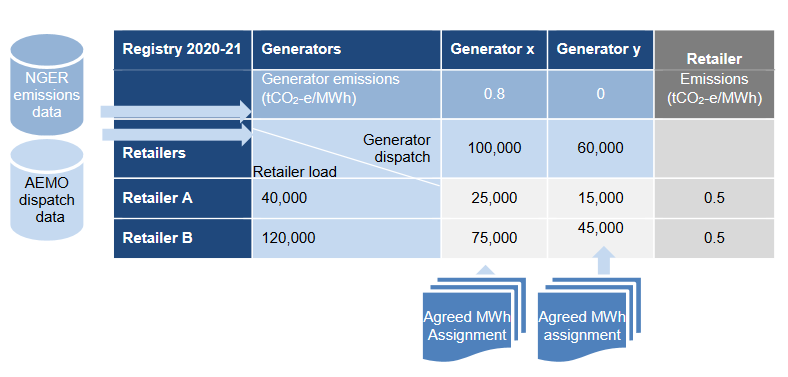
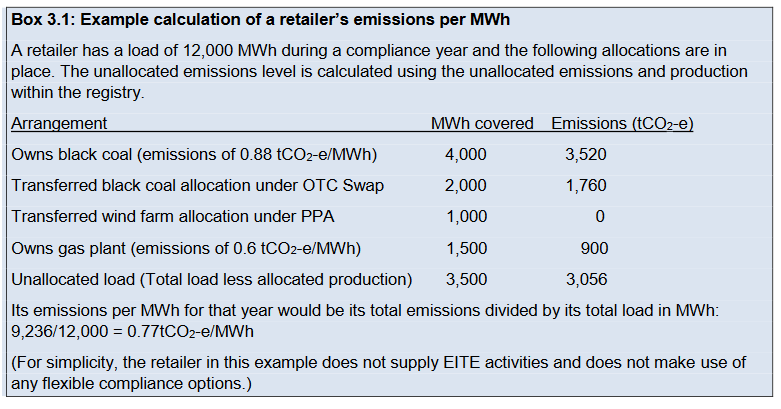 Source: NEG High-Level design document
Source: NEG High-Level design document
Beyond the simple examples above, the industry is likely to find a multitude of ways to efficiently transfer emissions obligations between parties. This form of approach both:
- encourages progressive changes to the generation stock, as investment in cleaner generation becomes relatively more attractive; and,
- at the margin, encourages the dispatch of cleaner existing generation ahead of more polluting.
These features compare favourably against environmental schemes that are not technology neutral or focus only upon subsidising new plant, such as the Renewable Energy Target, some forms of the Finkel Review’s Clean Energy Target, and renewable energy auctions.
The mechanism seems an efficient way to meet a given emissions target. Commentators appear to be progressively realising this, with most debate shifting to the target itself. This is actually a considerable step forward from where we were a year ago.
It’s not AEC’s role to buy into that fight, but we do acknowledge that the proposed target is at the low end and it seems inevitable that it will have to become stronger in time. When this occurs, the emissions guarantee mechanism will be ready to see it achieved. Importantly, the paper recommends a five-year notice of change in the target. Notice period is a critical part of investment certainty. Industry can tolerate ambition, but not surprise ambition.
Reliability Guarantee – How it works
The paper has taken the reliability mechanism considerably forward, with the proposal less radical than some of the options canvassed in the earlier consultation paper. Retailer’s obligations are to be met through financial instruments only, rather than having to identify generation sources and certify capacity as physically “dispatchable”. The Australian Energy Market Operator’s (AEMO) intervention powers will be limited to one year ahead of the period of concern and subject to independent scrutiny. These themes indicate a desire to reinforce the existing market’s reliability mechanism rather than replace it.
The paper describes an eight stage reliability guarantee process. In a nutshell, reliability is forecast into the future with the same tools as we have today. If, three years into the future, AEMO thinks the current stock of supply may not meet the reliability standard, the industry is put on notice that the guarantee may be triggered. If, with one year to go, a gap still exists, AEMO will invoke its powers as “Procurer of Last Resort”. This is similar in function to the existing Reliability and Emergency Reserve Trader (RERT), which it will supersede.
At this point, all retailers know they will have a reliability guarantee obligation against which they will have to demonstrate compliance at the end of the coming peak load period. After that period, the Australian Energy Regulator (AER) will review what each retailer’s demand was in conditions consistent with a high, but not extreme, peak demand period (i.e. a 1 in 2 year peak). The AER will then seek evidence that the retailer held sufficient financial contracts to remove their spot exposure to that peak demand. Those which did not hold sufficient contracts will face penalties, including bearing the cost of AEMO’s procurement of emergency reserves.
Underlying this approach is an assumption that behind every great financial contract is a great generator. Thanks to the NEM’s high price cap and participants’ risk management practices, this seems a fair assumption. It reinforces the existing approach where generator owners themselves decide whether their own plant can be relied upon at the time of peak, and take the risk of getting it wrong. This is preferable to relying on a central body, who face huge information asymmetries, from making this very difficult judgement.
AEMO will also provide a voluntary “book-build” service. This is effectively a dating site where developers of new generation can meet retailers.
Developing the model further
Last week took the model forward by adding a considerable degree of detail. There are still many steps to go, and the industry will continue constructively engaging throughout.
One unexpected feature that emerged last week is that the contracts that retailers may use to acquit their liabilities must be centrally cleared through a trading platform or reported to a trade repository. They cannot directly use owned generation in lieu of financial contracts.
This is presented as a pro-competitive measure and to enhance contract liquidity. Whilst these are worthy objectives, it is not yet clear how existing retailers with their own generation or have long-term power purchase agreements with them will be able to comply, and whether a reliability mechanism is the right place to address competition issues.
The Reliability Guarantee process can be found here.
Related Analysis
Certificate schemes – good for governments, but what about customers?
Retailer certificate schemes have been growing in popularity in recent years as a policy mechanism to help deliver the energy transition. The report puts forward some recommendations on how to improve the efficiency of these schemes. It also includes a deeper dive into the Victorian Energy Upgrades program and South Australian Retailer Energy Productivity Scheme.
2025 Election: A tale of two campaigns
The election has been called and the campaigning has started in earnest. With both major parties proposing a markedly different path to deliver the energy transition and to reach net zero, we take a look at what sits beneath the big headlines and analyse how the current Labor Government is tracking towards its targets, and how a potential future Coalition Government might deliver on their commitments.
The return of Trump: What does it mean for Australia’s 2035 target?
Donald Trump’s decisive election win has given him a mandate to enact sweeping policy changes, including in the energy sector, potentially altering the US’s energy landscape. His proposals, which include halting offshore wind projects, withdrawing the US from the Paris Climate Agreement and dismantling the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), could have a knock-on effect across the globe, as countries try to navigate a path towards net zero. So, what are his policies, and what do they mean for Australia’s own emission reduction targets? We take a look.
Send an email with your question or comment, and include your name and a short message and we'll get back to you shortly.



