EVs: The chicken and egg dilemma
A new US report released last week has refocused attention on the “chicken and egg” dilemma for the development of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure - no one wants to build it until there are more EVs needing it, and the motoring public is reluctant to buy EVs until they know there are more charging points.
The report, produced by the Rocky Mountain Institute, argues that now is the time to refocus on developing EV charging infrastructure because the EV “revolution” is here. In the US EV sales have been growing at a compound annual growth rate of 32 per cent in the past four years and monthly sales data for this year “suggests that the sales rate is accelerating sharply”[i]. It projects that there could be 2.9 million EVs on US roads within five years, which will require more than 11,000GWh of electricity, equivalent to about $1.5 billion in electricity sales.
Car prices, limited model options and range anxiety have long been a block to EV take-up, but those impediments are set to fall within a few years, the institute argues. “EVs are already cheaper to refuel and in some cases, such as high-usage fleet vehicles, they are cheaper to own conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.”
High use fleet vehicles are prime candidates for electrification. The report says that the total cost of ownership is already lower for EVs than for conventional ICE vehicles.
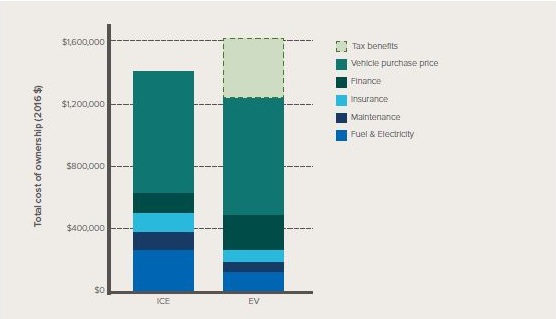
The five-year total cost of operation (assuming a discount rate of 10 per cent) for a fleet of 30 Chevy Bolts driving 25,000 miles per year (around 40,000 kms) compared to the cost of running a fleet of 30 compact cars, based on average fleet costs and performance is shown in Figure 1. The main savings from EVs are in their lower maintenance and fuel costs, while their purchase price is higher, as can be seen in Table 1. There is also a substantial benefit from tax credits, but the Institute argues that as battery costs decline and production volume increases, the credits will no longer be needed.
Figure 1: Five year total cost of ownership net present value for a fleet of 30 vehicles in Colorado, ICE vs EV
Source: Rocky Mountain Institute
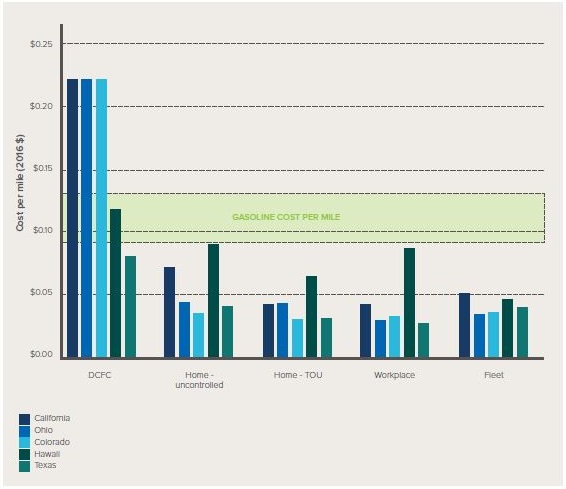
In the five US states considered by the “From Gas to Grid” report – California, Colorado, Hawaii, Ohio and Texas - the cost of charging an EV ranges from $0.03 cents/mile (around 1.8 cents per kilometre) to $0.22 cents/mile (around 13.5 cents each kilometre), compared to a petrol cost of between 0.09 cents-0.13 cents.
Figure 2: Retail cost to EV owner, or employer of EV owner, to charge one mile of EV range under different utility tariffs and DCFC programs
Source: Rocky Mountain Institute
The spread of costs by state is:
- Southern California – from $0.04/mile if charged during workday hours at a workplace and as high as $0.22/mile if using a public DC fast charging network.
- Colorado – from $0.03/mile if charged at home during the off-peak hours of a TOU rate, up to $0.22/mile if using a public DCFC.
- Ohio – from $0.03/mile if charged at work to $0.22/mile if using a public DCFC.
- Texas – based on the cost in Austin is from $0.03/mile if charged at work to $0.08/mile using a DCFC (largely due to Austin Energy’s Plug-in Everywhere network which offers low cost public charging for EV owners).
- Hawaii – from $0.05/mile for fleet vehicles, $0.06 if personally owned and charged at home through to $0.011 if using a public DCFC.
The take-up of EVs in each state is shown below, along with the level of charging infrastructure available.
Table 1: EV Takeup by US State and Charging Infrastructure Per Vehicle
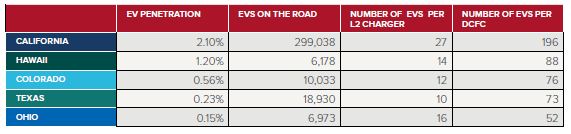
Source: Rocky Mountain Institute
There are three types of charging available for EVs:
Level 1 – plugging into a conventional electrical socket and using the vehicle’s inbuilt converter. Can take up to 14 hours to charge.
Level 2 – dedicated rechargers that can be installed at home or other venues. Take up to eight hours to charge. They are suited to charging overnight or where a vehicle is parked for an extended period, such as a workplace or shopping centre.
Level 1 – DC Fast Charging (DCFC) stations. Can provide a substantial recharge for an EV in around 20-30 minutes.
In Australia most publicly accessible chargers provide power for free, but this is expected to change as more infrastructure is rolled out. Exceptions include a handful of paid stations in South Australia and one in NSW on the ChargePoint network, and the RAC's 'Electric Highway' in Western Australia, which runs from Perth to Margaret River in the state’s south-west[ii]. The cost of recharging at the RACWA points is set at 45 cents/kWh, plus $1 per charging session.
ChargePoint, an international commercial EV plug-in charging network, expects the roll-out of DCFC’s in strategic locations like petrol stations to accelerate over the next two to three years particularly on the Melbourne-Brisbane corridor on the east coast and in the urban fringe areas.
Existing charging infrastructure for both the US and Australia can be found here
[i] From Gas to Grid. Building charging infrastructure to power electric vehicle demand. Rocky Mountain Institute
[ii] https://www.choice.com.au/transport/cars/eco-friendly/articles/charging-electric-cars
Related Analysis
The return of Trump: What does it mean for Australia’s 2035 target?
Donald Trump’s decisive election win has given him a mandate to enact sweeping policy changes, including in the energy sector, potentially altering the US’s energy landscape. His proposals, which include halting offshore wind projects, withdrawing the US from the Paris Climate Agreement and dismantling the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), could have a knock-on effect across the globe, as countries try to navigate a path towards net zero. So, what are his policies, and what do they mean for Australia’s own emission reduction targets? We take a look.
UK looks to revitalise its offshore wind sector
Last year, the UK’s offshore wind ambitions were setback when its renewable auction – Allocation Round 5 or AR5 – failed to attract any new offshore projects, a first for what had been a successful Contracts for Difference scheme. Now the UK Government has boosted the strike price for its current auction and boosted the overall budget for offshore projects. Will it succeed? We take a look.
Energy transition understanding limited: Surveys
Since Graham Richardson first proposed a 20 per cent reduction in Australia’s greenhouse gas emission levels in 1988, climate change and Australia’s energy transition has been at the forefront of government policies and commitments. However, despite more than three decades of climate action and debate in Australia, and energy policy taking centre stage in the political arena over the last decade, a reporting has found confusion and hesitation towards the transition is common among voters. We took a closer look.
Send an email with your question or comment, and include your name and a short message and we'll get back to you shortly.